Student Information
DNA Replication Overview
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. This is the first step in the Central Dogma (DNA → RNA → Protein) and is essential for cell division (mitosis and meiosis) and the inheritance of genetic information.
The Semi-Conservative Model
The Meselson-Stahl experiment (1958) confirmed that DNA replication is semi-conservative.
- What it means: Each newly synthesized DNA molecule consists of one "old" strand (from the parent molecule) and one "new" strand (newly built).
Key Enzymes and Proteins
| Enzyme/Protein | Function |
|---|---|
| Helicase | The "unzipper." Unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds. |
| Single-Strand Binding Proteins (SSBs) | Coat the separated DNA strands to prevent them from re-annealing. |
| Topoisomerase | Relieves the supercoiling and torsional strain ahead of the replication fork. |
| Primase | Builds a short, complementary RNA primer for DNA Polymerase to start from. |
| DNA Polymerase III | The main builder. Adds DNA nucleotides to the 3' end of the primer. |
| DNA Polymerase I | Removes the RNA primers and replaces them with DNA nucleotides. |
| DNA Ligase | The "gluer." Seals the nicks in the DNA backbone between Okazaki fragments. |
The Process of DNA Replication
Stage 1: Initiation - Replication begins at specific sites called origins of replication.
Stage 2: Elongation - New DNA strands are synthesized. The leading strand is synthesized continuously, while the lagging strand is synthesized in short fragments called Okazaki fragments.
Stage 3: Termination - Replication ends when replication forks meet.
DNA Replication: Leading and Lagging Strands
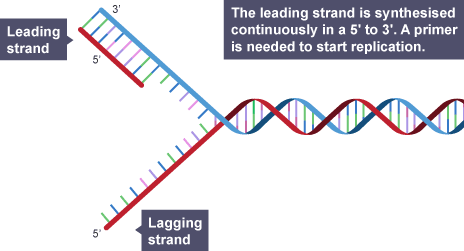
DNA replication showing leading and lagging strands
The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5' to 3' direction. A primer is needed to start replication.
The lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in short Okazaki fragments, each requiring its own primer.
Telomeres and The End-Replication Problem
Telomeres are long, non-coding, repetitive nucleotide sequences at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes that protect against the loss of genetic information during replication.